Fungal Eye Infections: Types, Symptoms, Treatment, and Surgery
The eye is a sensitive and essential organ, and many infections can affect its functioning. A fungal eye infection occurs when a fungus enters the tissues of the eye, posing a hazardous threat that requires immediate medical attention to avoid severe consequences.
Types: Various fungal species, such as Aspergillus, Fusarium, Candida, and others, can cause eye infections, leading to different types of fungal eye diseases.
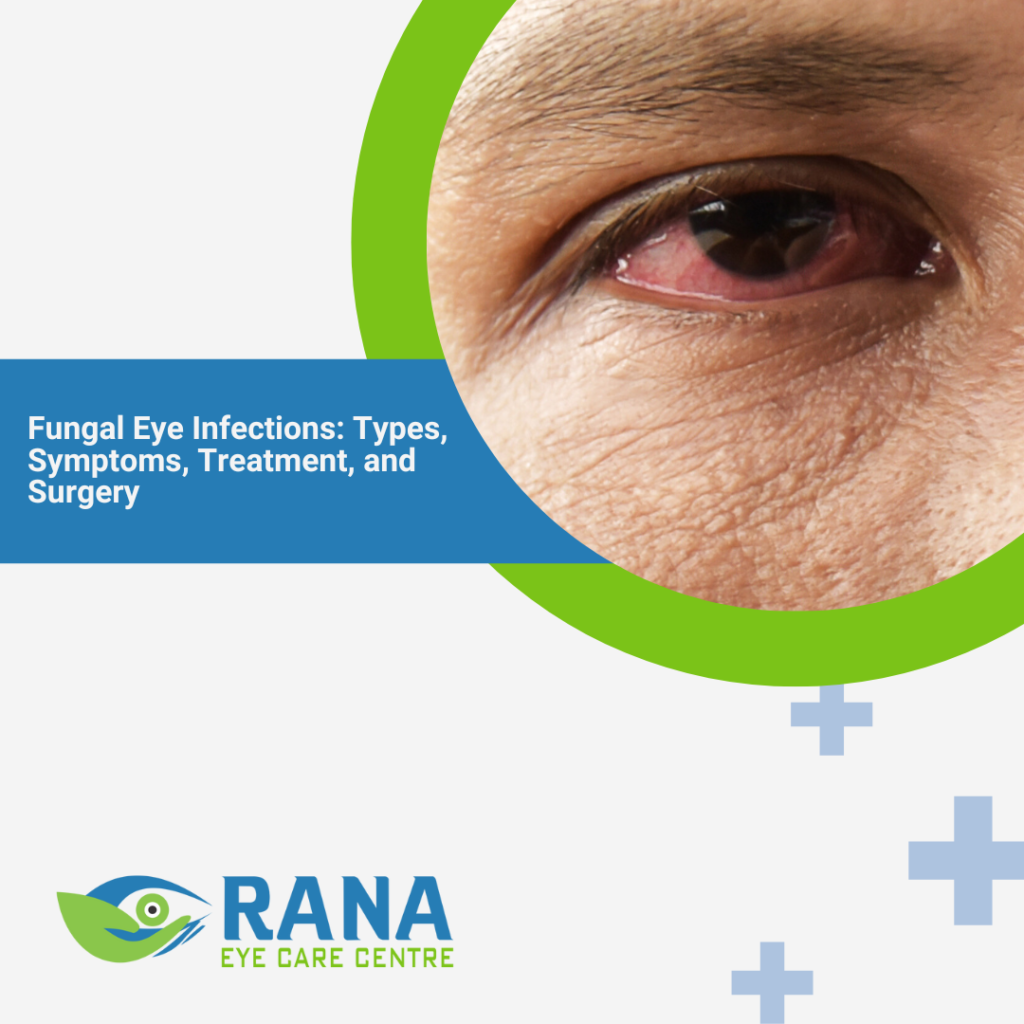
Symptoms of a fungal eye infection include: Fungal keratitis, also known as fungal eye disease, occurs when a fungus infiltrates the cornea—the transparent, dome-shaped surface covering the front of the eye. Diagnosing ocular yeast infections can be challenging since their symptoms often resemble those of other eye infections. Typical symptoms include eye pain, redness, poor vision, photophobia, excessive tearing, eye discharge, and a feeling of a foreign object or sand in the eye. Seeking immediate medical attention is crucial if any of these symptoms develop, as delaying treatment can result in serious side effects, including vision loss.
Treatment: A combination of antifungal medications, such as eye drops, ointments, or oral drugs, is often used to treat fungal eye infections. The specific fungus involved and the severity of the infection will determine the recommended antifungal medication. It is imperative to follow the prescribed regimen and complete the treatment to ensure complete eradication of the fungus.
Surgery: In extreme cases or when the infection does not respond to topical treatment, surgery may be necessary. The goal of surgery is to remove infected tissue and promote healing. Depending on the disease’s severity, procedures such as corneal debridement, where infected tissue is removed, or corneal transplantation, where a healthy cornea from a donor replaces the infected one, may be performed.
Corneal Transplant (Keratoplasty): Fungal invasion can cause significant damage and scarring to the cornea, leading to vision loss. In some cases, a corneal transplant may be required to restore vision and prevent further complications. This surgical procedure involves removing the damaged cornea and replacing it with a healthy cornea obtained from a donor. Corneal transplant surgery can effectively treat the symptoms of a fungal eye infection and restore vision.
Conclusion: Fungal eye infections can pose a serious threat to eye health and vision. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications. While most cases are treated with antifungal medications, severe infections may necessitate surgery. If you notice any symptoms of a fungal eye infection, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. Always prioritize your eye health and seek professional help promptly.



No Comments