Know All About Ametropia – Refractive Error
Ametropia means that the shape of your eye does not bend light correctly, resulting in a blurred image.
Also known as a condition of refractive error, refers to vision disorders in which the parallel rays of light coming from infinity (when accommodation relaxed) are not focused in the sensitive layer of retina means that they are focused either behind or front in one or both the meridians.
Symptoms
- Blurred vision
- Asthenopia
- Headache
- Difficulty reading or seeing up close
- Crossing of the eyes in children (esotropia)
- Poor concentration
- Avoidance of near work
The four main types of refractive error which are:
- Myopia (nearsightedness),
- Hyperopia (farsightedness),
- Astigmatism
- Presbyopia (loss of near vision with age).
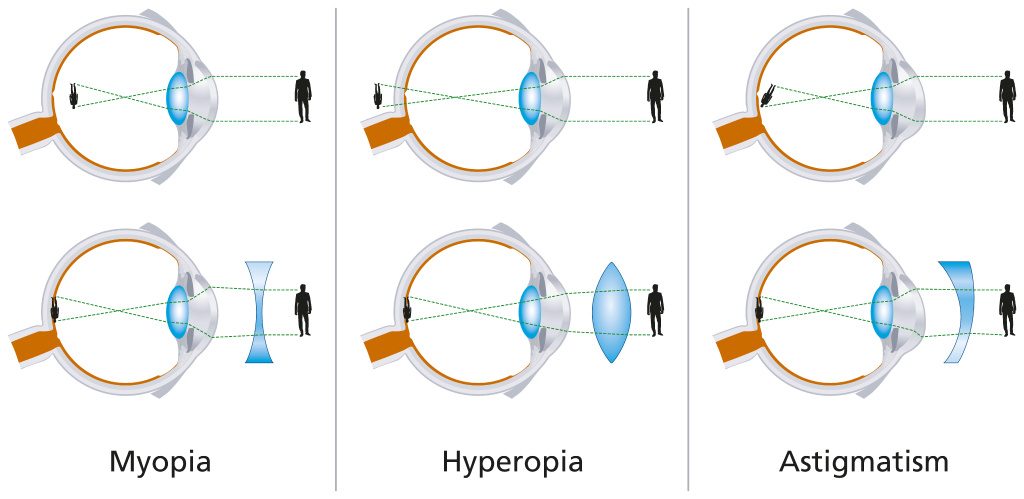
- Myopia also known as nearsightedness. It is the error of refraction where the parallel light rays coming from infinity into the eye are focused in front of the retina instead of on it when accommodation is relaxed. People with this condition mainly complain of poor distance vision or they cannot recognized people who are far away .Myopic people often find that they vision becomes worse at night or in dim light. Myopia usually starts early in life and typically increases between the ages of 12 and 30.
- Hyperopia is also called long –Sightedness and it is the refractive error where the optical system of the eye focuses the parallel rays from infinity behind retina rather than on retina with accommodation relaxed. It can be inherited. An individual complain of difficult for blurred vision at near but clear vision at far for mild hyperopia while people complain of blurred vision at near as well as at far for moderate and high hyperopia.It is also associated with asthenia symptoms due to sustained accommodative efforts. Hyperopia in children may cause the eye to turn (Crossed eye).The symptoms of hyperopia may get worse with age.
- Astigmatism is a type of refractive error where the parallel rays of light enter the eye (with accommodation relaxed) and do not come to a single point focus on or near the retina. Astigmatism results to distortion of the object’s image .Usually, astigmatism causes blurred vision at all distances. The symptoms of astigmatism don’t change much with age.
- Presbyopia refers to eye sight of old age. It is not refractive error but a condition of physiological insufficiency of accommodation due to natural aging changes in the eye that lead to progressive fall in near vision. Also can defined as decrease in the amplitude of accommodation or loss of accommodative ability with age. Unlike myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism affect only some people, Presbyopia is a condition for all people as they get old as it is due to natural hardening of crystalline lens which makes it more difficult and eventually impossible to accommodate. Usually begins to be a problem after 40 or 45 years old and slowly get worse until about 60 years. Usually people’s main complaint is difficulty in near vision (difficulty in reading small prints or difficulty in threading needle) associated with asthenia after reading or doing any near task.
Detection of refractive error
Refractive error can be diagnosed by an eye care professional through a routine eye examination of patients who consult the eye clinic/ eye hospital or through vision screening of the population at large which is most commonly carried out on schoolchildren. Special imaging or other further investigations which can be required where is necessary are. Auto refraction, Radioscopy, keratometry, Subjective refraction and Jackson cross cylinder.
Management of Ametropic eye
Refractive disorders are easily treatable by appropriate refractive correctioned. And this should be detected and corrected as soon as possible because these can lead to permanent vision problem. For example: High refractive error in child may lead to amblyopia (lazy eye), Retinal problem and progresses towards blindness.
Corrective eyeglasses: Most commonly used
- Convex or plus lenses for hyperopia
- Concave or Minus lens for myopia
- cylinder lenses, sphero-cylinder /Toric lens for astigmatism
Corrective contact lenses
- Contact Lens (soft , RGP,) for Myopia and Hyperopia
Ortho-k(refers to the temporarilyreshape the cornea by using overnight contact lens usually gas permeable contact lenses to decrease refractive errors such like Myopia, Hyperopia and astigmatism.
- Toric soft contact lens and toricrigid gas permeable contact lens for astigmatism
Refractive surgery
- Laser in-situ keratomileusis(LASIK)
- Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)
Complications and impact of refractive error
Myopia is the most common leads to severe complications especially when is uncorrected:
- Ocular infections due to microbes which can be introduced by rubbing the eyes, which is often done to get relief from fatigue and tiredness.
- Accommodative convergent squint ( usually from hyperopia)
- Amblyopia ( from Anisometropia)
- Myopia can cause Retinal detachment
- Pathological myopia
- Complicated cataract
- Vitroushaemorrhage
- Choroidalhaemorrhage
- Strubismusfixus convergence
- Blindness
Refractive error, if uncorrected, it results in an impaired quality of life of people, irrespective of their age, sex and ethnicity as it has negative impact on self-esteem, career choice, and ocular health. In that case must visit the best Opthamologist or eye care hospital in your area.
References
http://www.med.umich.edu/1libr/Ophthalmology/comprehensive/RefractiveErrors.pdf
https://www.umkelloggeye.org/conditions-treatments/refractive-errors



No Comments